You can also add to your health journal encourading news about advances in the heart disease management. Here are some of them:
Gene therapy prototype for heart muscle regeneration created.

American molecular biologists from the Mount Sinai School of Medicine in 2025 developed a gene therapy capable of restarting the process of cardiac muscle regeneration by activating the CCNA2 gene, which is responsible for myocardial formation during embryonic development. The scientists used the Ad5 adenovirus to deliver a modified version of the CCNA2 gene to the patient's cells. As a result, the gene therapy even induced the division of cardiomyocytes obtained from a 55-year-old volunteer and the cell division did not lead to a deterioration in their function or negative changes in their structure. The scientists achieved similar results in experiments on transgenic mice, raising hopes for the rapid start of clinical trials of this therapy in human volunteers.
A patch for treating heart failure developed in Germany.
German scientists from the University Medical Center Göttingen in 2025 have transplanted lab-grown cardiac muscle into patients with heart failure for the first time. The EHM patch is lab-grown cardiac muscle. It consists of cardiac cells derived from induced pluripotent stem cells (capable of developing into different tissue types). These cells are embedded in a collagen hydrogel. Before moving on to clinical trials, the technology was tested in rhesus macaques, simulating real-world treatment. The researchers found that implantation of these "patches," containing up to 200 million cells, helps restore cardiac function by forming new cardiac tissue. Imaging methods and sample analysis showed that the transplanted cells successfully engrafted when the immune response was suppressed and improved the heart's pumping function. So far, this is the only way to safely and permanently deliver cardiomyocytes (heart muscle cells) to the damaged organ.
Heart drug Mavacamten passed clinical trials
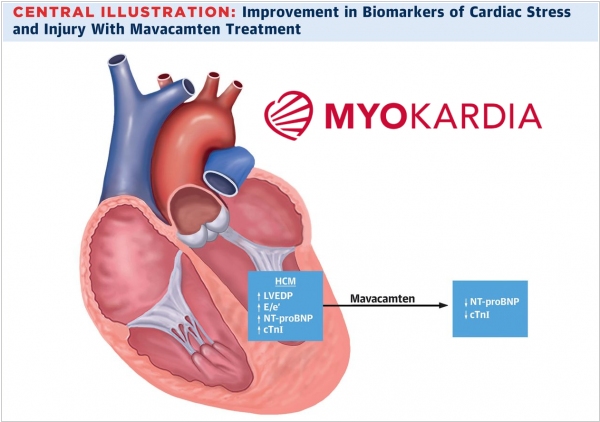
American company MyoKardia in 2020 presented the long-awaited results of Phase 3 clinical trials of Mavacamten for the treatment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (thickening of the ventricular walls, which increases tone and reduces the effectiveness of heart contractions). Mavacamten is a first-in-class drug that acts as a myosin inhibitor, disabling several cellular motors in heart muscle tissue. It helps heart to relax, fill with blood and beat more effectively. Certification of the drug in the US is scheduled for the first quarter of 2021.
Bayer is using artificial intelligence to find new drugs to treat cancer and heart disease.
Pharmaceutical giant Bayer in 2020 has partnered with Exscientia, a British startup developing an AI-powered drug discovery system. As part of this partnership, the German giant was implementing its partner's solutions to research compounds that could potentially become drugs for cardiovascular and oncological diseases. The companies also collaborated on early-stage research projects combining Exscientia's drug discovery platform with Bayer's data collection capabilities. Exscientia received $266 million in investment from Bayer to develop new projects. The companies believe that artificial intelligence can accelerate drug discovery and improve the quality of drug development, while reducing the cost of research.
